Delta 8 and the Brain: What’s Really Going On?
Delta 8 and the Brain: What’s Really Going On?
Jun 14, 2025
Roughly 1 in 6 U.S. adults have now tried Delta 8 THC, with over half reporting its effects as less intense, more manageable, and clearer-headed than traditional Delta 9 THC, according to a peer-reviewed study published in Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research.
That data point isn’t just a trend, it’s a sign that something fundamentally different is happening in the brain when people use Delta 8. Unlike its more potent cousin, Delta 9, Delta 8 interacts with the brain in a subtler, often more favorable way. Users consistently report a sense of calm focus, mild euphoria, and noticeably reduced anxiety or paranoia. But what’s actually driving those effects inside the brain? What’s happening at the receptor level, and why does it feel so different - especially for people sensitive to traditional THC?
Understanding Delta 8’s neurological profile means looking closely at how it engages with the body’s endocannabinoid system, particularly the CB1 receptors concentrated in the brain’s emotion and cognition centers. The science is still emerging, but early evidence and user-reported experiences are painting a clearer picture of how Delta 8 shifts mental states without overpowering them.
In this article, we’ll explore the brain-level science behind Delta 8’s effects - from how it works in key neural pathways to what researchers are starting to uncover about its potential therapeutic benefits.
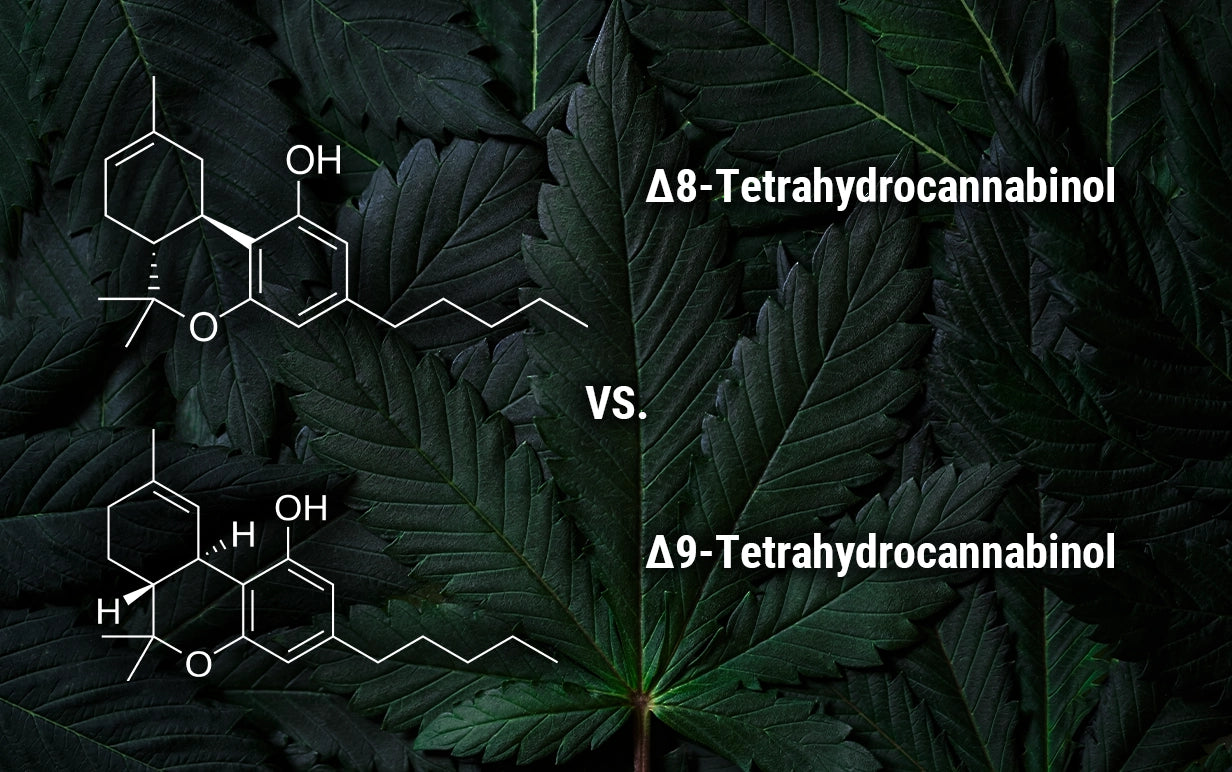
A Quick Primer on Delta 8 THC
Delta 8 THC is a naturally occurring minor cannabinoid found in trace amounts within hemp plants. What sets it apart isn’t just its chemistry, it’s the way it delivers psychoactive effects without tipping into overstimulation. As a structural isomer of Delta 9 THC, Delta 8 shares a nearly identical molecular makeup, with just one bond shifted. That small difference translates to notably different effects on the brain.
Under the 2018 Farm Bill, Delta 8 is federally legal when derived from hemp and contains less than 0.3% Delta 9 THC. However, some states have enacted restrictions, and the lack of federal regulatory oversight means product quality can vary, making third-party testing essential.
How It Differs from Delta 9
Delta 8 binds to the same CB1 receptors in the brain that Delta 9 targets, but it does so with less intensity. It acts as a partial agonist, meaning it stimulates the receptor without fully activating it. Delta 9, by contrast, is a full agonist, flooding the receptor and often triggering stronger psychoactive responses, including anxiety or mental fog in some users.
This gentler binding profile means Delta 8 delivers more balanced effects, lighter euphoria, more clarity, and fewer episodes of paranoia. From a brain-chemistry standpoint, this difference in receptor activity helps explain why users often describe Delta 8 as “functional” or “daytime-friendly.” It nudges the brain’s cannabinoid system without overwhelming it, creating a psychoactive experience that feels smoother and more predictable.
How the Brain and Endocannabinoid System Work Together
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) functions as the brain’s chemical traffic controller. It’s not just about cannabis, it’s a core biological system that regulates essential processes like mood, memory, appetite, pain perception, and sleep cycles. Discovered in the early 1990s, the ECS consists of three key parts: endocannabinoids (naturally produced compounds similar to THC), enzymes that break them down, and receptors, mainly CB1 and CB2.
CB1 receptors are concentrated in the central nervous system, especially in brain regions tied to emotional regulation, sensory perception, and cognitive processing. CB2 receptors, by contrast, are mostly located in immune tissues and peripheral organs. The balance between these two receptor types plays a central role in how cannabinoids like Delta 8 influence the brain and body.

What Happens in the Brain When You Use Delta 8
When Delta 8 enters the bloodstream, it binds to CB1 receptors, but only partially. This matters. Unlike Delta 9, which fully activates these receptors and can overwhelm them, Delta 8’s partial agonist behavior leads to subtler, more controlled changes in neural signaling.
Key areas involved include:
-
The amygdala, where emotional responses are processed
-
The prefrontal cortex, responsible for decision-making and attention
-
The hippocampus, which governs memory formation
In these regions, Delta 8 modulates activity without overstimulation. Instead of flooding the ECS, it provides a measured signal, which may explain why users often feel a gentle lift in mood or clarity without dissociation or racing thoughts.
This milder activity also affects how neurotransmitters like glutamate and GABA behave, both of which are vital for maintaining balance in excitatory and inhibitory brain signaling. While Delta 9 often disrupts this balance, Delta 8 appears to fine-tune it, nudging the brain toward calm focus rather than intense psychoactivity.
The result? A pharmacological profile that allows Delta 8 to engage with the ECS in a more adaptive way, stimulating change without destabilizing the system. That’s not just anecdotal. It reflects the distinct receptor dynamics that make Delta 8 neurologically different from Delta 9 at a functional level.
Cognitive and Emotional Effects of Delta 8
Delta 8’s interaction with the brain doesn’t just affect mood or perception in a general sense, it triggers specific, noticeable changes that many users describe as mentally grounding and emotionally stabilizing. These effects tend to stand apart from the intensity of Delta 9, offering a more measured experience that fits better into daily life. Let’s break down how Delta 8 influences three key cognitive and emotional areas: mood and anxiety, focus and clarity, and memory and perception.

Mood and Anxiety
One of the most commonly reported reasons people turn to Delta 8 is to manage stress and anxiety, but without the overstimulation or mental spiraling often associated with Delta 9. What makes this possible is Delta 8’s more restrained effect on key neurotransmitter systems, particularly those involving dopamine and serotonin.
By gently interacting with CB1 receptors, Delta 8 appears to modulate the release and uptake of these mood-related chemicals rather than flood the system. This subtle rebalancing may contribute to a stabilizing effect on emotional state, users often describe feeling “centered” or “less reactive” rather than sedated. It’s not a mood lifter in the conventional sense, but a downshift from heightened emotional reactivity, which makes it especially appealing for those who experience anxiety from traditional THC products.
Focus and Clarity
Unlike Delta 9, which can lead to racing thoughts or fragmented attention, Delta 8 is frequently associated with sustained mental clarity and reduced cognitive noise. For some, it feels more like a mental “decluttering” than a high.
In informal surveys and user reports, people describe Delta 8 as helpful for tasks that require focus without emotional interference, writing, strategizing, or simply staying present. The lack of paranoia - a common side effect of Delta 9 - is a major factor. This makes Delta 8 particularly attractive for daytime use, especially in low to moderate doses where its cognitive effects stay sharp rather than hazy.
Memory and Perception
Delta 8 does influence short-term memory and sensory perception, but in ways that tend to feel more subtle and manageable than Delta 9. At higher doses, users may notice slight shifts in how time feels or how sensory input is processed, colors more vivid, sounds more immersive, but without the disorientation that often accompanies stronger THC products.
Memory effects, if present, are typically described as mild short-term fog rather than full lapses or blackouts. This lighter cognitive footprint is largely due to Delta 8’s partial activation of CB1 receptors in the hippocampus, the brain’s memory hub. The result is a psychoactive experience that’s easier to stay aware within, especially for users who prioritize control over intensity.
Potential Neuroprotective or Therapeutic Benefits (Emerging Research)
Although Delta 8 is primarily marketed for its psychoactive effects, early preclinical studies suggest it may hold potential beyond recreation, particularly in neuroprotection and symptom relief.
A 1995 study funded by the National Cancer Institute found that Delta 8 significantly reduced nausea in pediatric cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, with minimal side effects. This discovery led researchers to examine Delta 8’s broader interactions with inflammation and brain function.
In rodent models, Delta 8 has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties in the central nervous system. These studies show reduced neuroinflammation and oxidative stress markers, two biological processes linked to neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Some experiments also indicate Delta 8 may inhibit overactive neural pathways, offering a protective buffer against excitotoxicity, a form of neuronal damage caused by excessive stimulation.
Importantly, these studies involve non-human subjects, and the mechanisms observed in rodents may not fully translate to people. Still, the early findings are promising enough to justify further exploration into Delta 8’s potential as a therapeutic agent, especially for conditions where inflammation and neurotransmitter imbalance play a role.
What We Don’t Know Yet
Despite growing interest, the science around Delta 8 remains fragmentary. There are no large-scale human trials examining its long-term effects on brain health, and much of what we assume comes from extrapolated data, either from Delta 9 research or anecdotal user reports.
This creates a gap between public perception and scientific certainty. While many users report relief from anxiety, pain, or nausea, Delta 8 is not an FDA-approved treatment for any condition. It should never be substituted for clinical care or prescription medication.
As with any emerging compound, realistic expectations are key. Delta 8’s therapeutic promise is still just that, a promise, not a proven solution. Ongoing research will be critical to determine whether its neuroprotective effects hold up in human populations and under controlled conditions.

Safety, Tolerance, and Brain Health Considerations
Current evidence suggests no known neurotoxicity from Delta 8 THC at moderate, controlled doses. However, the real concern lies not in the compound itself, but in the market conditions surrounding it. Because Delta 8 is often synthesized from CBD in loosely regulated environments, products can vary widely in purity, potency, and safety.
Some batches have been found to contain residual solvents, heavy metals, or synthetic byproducts, all of which carry far more risk than Delta 8 itself. That’s why sourcing from brands that publish full-panel Certificates of Analysis (COAs) is non-negotiable. Moonwlkr, for example, provides transparent third-party lab results for every product batch, ensuring consumers aren’t unknowingly inhaling or ingesting contaminants.
Tolerance and Long-Term Use
Like all THC-based cannabinoids, Delta 8 can lead to tolerance buildup, especially with consistent daily use. Users may find effects diminishing over time, not because the product has changed, but because CB1 receptors downregulate in response to repeated stimulation.
To counter this, many rely on smart-use strategies like:
-
Microdosing, which maintains efficacy while reducing cumulative load
-
Tolerance breaks, allowing receptor sensitivity to reset
-
Dose cycling, which varies intake days to prevent saturation
While Delta 8’s intensity is lower than Delta 9, chronic high-dose use still carries risks, particularly for cognitive sharpness and emotional regulation over time. Managing frequency and dose is key to sustaining benefits without unwanted neurological side effects.
Final Thoughts: What Delta 8 Is Doing in Your Brain
Delta 8 engages the brain in a way that feels intentional rather than overwhelming. By partially activating CB1 receptors, it promotes a sense of calm alertness, without triggering the racing thoughts, anxiety, or fogginess often associated with Delta 9.
For people seeking mental balance without mental overload, it offers a middle ground: psychoactive enough to shift perception, but controlled enough to maintain self-awareness. Still, its safety hinges on product quality and responsible use.
That’s where sourcing matters. Moonwlkr’s third-party tested Delta 8 products give users the confidence of knowing exactly what’s in each dose, making exploration safer, smarter, and more consistent.

